At the Centre for Children’s Gut Health, we are at the forefront of single-cell research in paediatric gastroenterology, using cutting-edge technologies to chart the cellular landscape of the human gut in health and disease.
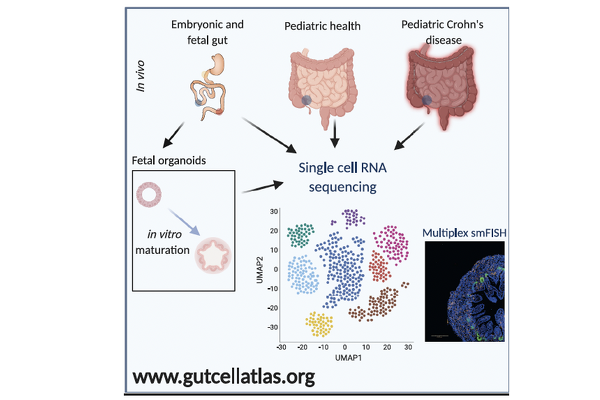
In a landmark study published in Developmental Cell (Elmentaite, Ross, Zilbauer et al., 2020), our team performed single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) across the developing human intestine and identified striking parallels between epithelial gene expression in the fetal gut and in children with Crohn’s disease. This work revealed that chronic inflammation in paediatric IBD reactivates fetal transcriptional programmes — a phenomenon with profound implications for understanding barrier dysfunction and epithelial remodelling in early-onset disease.
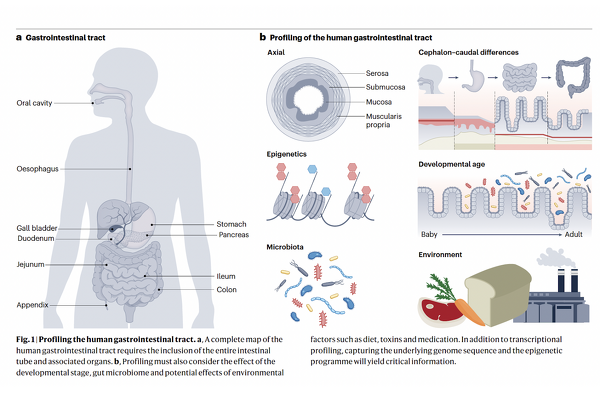
Building on this, Professor Zilbauer co-led the Human Cell Atlas (HCA) Gut Bionetwork and co-authored a major roadmap paper in Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology (Zilbauer et al., 2023), which outlines a strategic framework for creating a comprehensive human gut cell atlas. This includes spatial and temporal mapping, cross-disease comparison, and integration with genetic and multi-omic data.
Our group also contributed to the HCA’s landmark efforts in mapping the intestinal tract across developmental stages, as reported in Nature (Elmentaite et al., 2021), and more recently to a large-scale meta-analysis (Oliver et al., Nature, 2024) identifying shared cellular signatures across diverse inflammatory gut diseases — including metaplasia and loss of homeostatic cell types.
These studies have shown that:
Our continuing efforts aim to apply these insights directly in the clinic — integrating single-cell signatures with organoid models and biomarker platforms to enable personalised diagnostics and targeted treatment for children with IBD and other chronic gut disorders.
Key Publications: